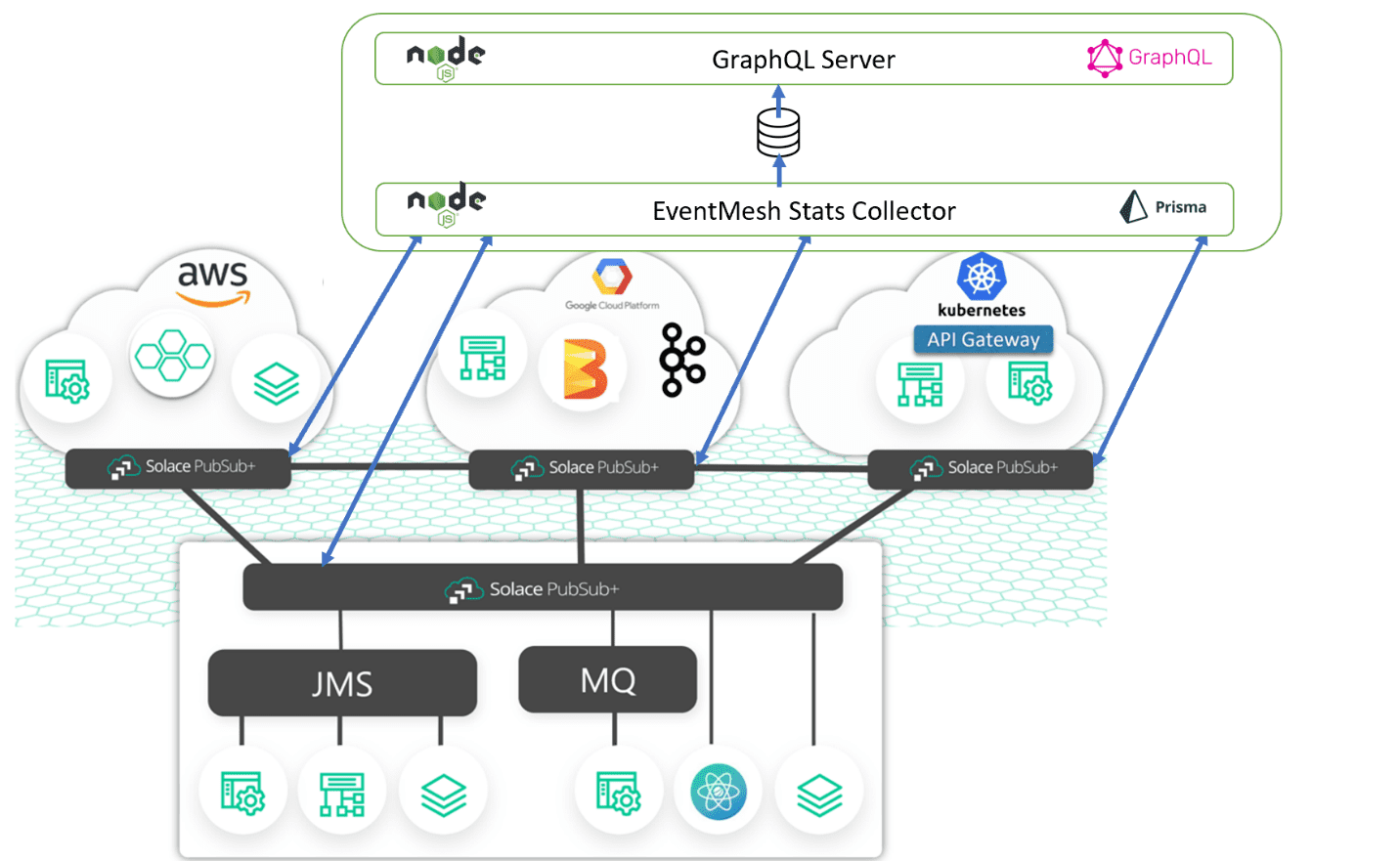
In this blog post, I will explain how you can leverage the power of GraphQL’s extensible API model to better understand the architecture and state of your event mesh. An event mesh is an interconnected network of event brokers that distributes events among decoupled applications, cloud services and devices, anywhere in the world and running in any cloud, edge or on-premises environment.
Here’s the high-level architecture of an event mesh:
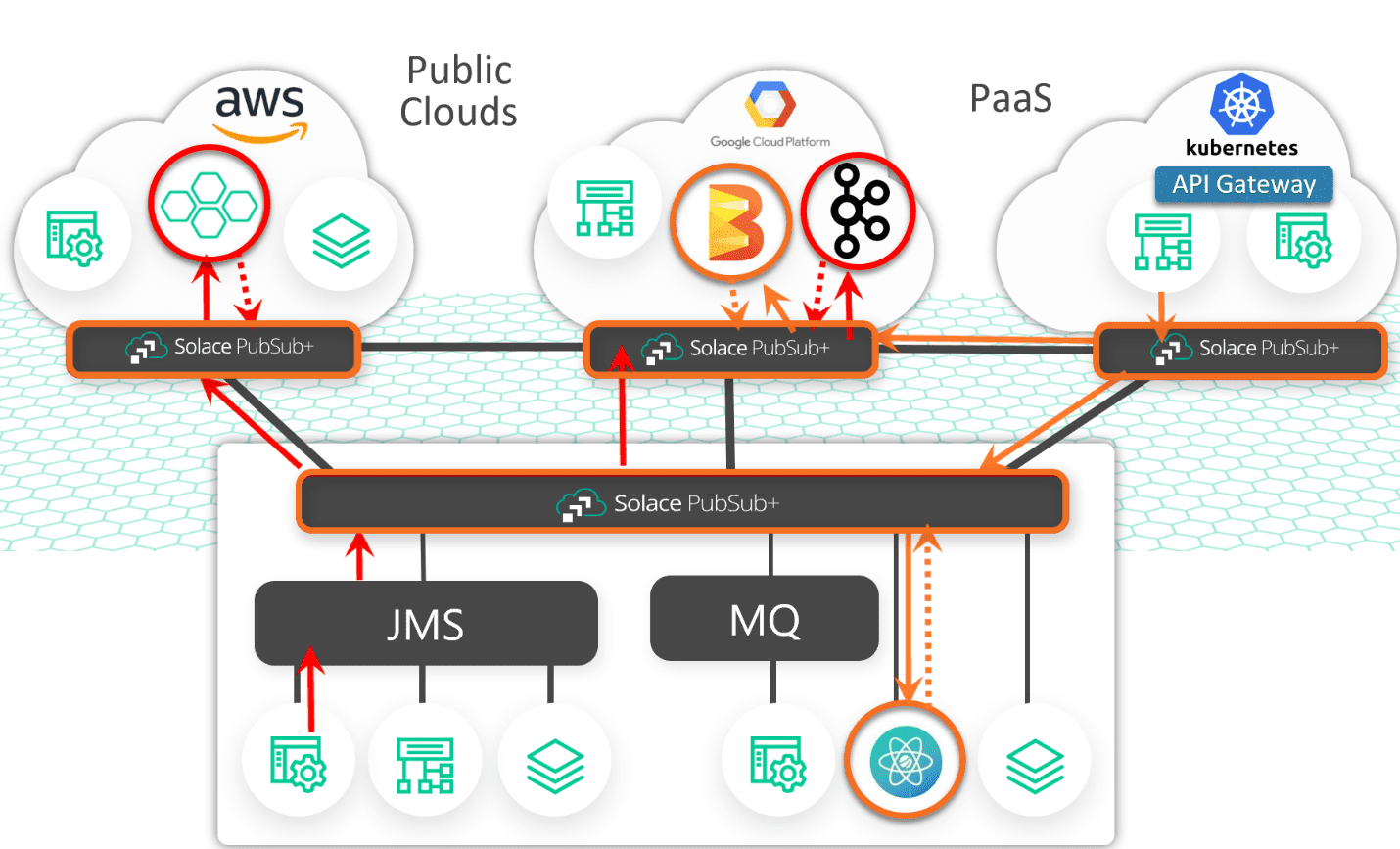
In this diagram, you have a network of Solace PubSub+ Event Brokers deployed on-prem, in public clouds, and even in a private cloud. They link together via a protocol called dynamic message routing (DMR). The key thing to understand about DMR is that events will only get routed to where they need to go without the need to pre-define the path or the routing rules.
For example, if you have an Apache Beam\Google Cloud Dataflow microservice producing an event in Google Cloud Platform and you want it to be routed to a microservice in AWS, all the microservice in AWS has to do is express interest in the Beam\Dataflow event via a ‘Topic Subscription’.
REST-ful API to manage/monitor PubSub+ Event Broker
A core component of the event mesh is the event broker. Solace’s PubSub+ Event Broker is a multi-protocol event broker that comes in multiple form factors – hardware appliances, software, and as a service. The event broker handles client connectivity to the event mesh and also routes data to the neighboring nodes in the event mesh.
Every PubSub+ Event Broker exposes a REST-ful management interface – called the Solace Element Management Protocol (SEMP) – that gives you access to various internal statistics and administrative functions for the event broker.
For example, by running a SEMP query against a broker, you can figure out which IP-Addresses/users are connected to the broker. Another query will give you an understanding of which Topic Subscriptions are active on a broker.
GraphQL as an Abstraction Layer on Your Event Mesh
Solace has monitoring solutions, such as Solace PubSub+ Monitor and PubSub+ Insights built on top of the SEMP API and along with gathering logs, but we will be using GraphQL to extend the SEMP API.
By taking advantage of the SEMP API, you can periodically poll all the nodes of your event mesh to store statistics in a database. You can then use a GraphQL server to front the results of the database and can build out an expressive API that will allow you to answer questions such as :
- Which node has a subscription active on a specified topic?
- Which user(s) is subscribing to a specific topic?
- Which links of my event mesh are experiencing the most traffic?
- Which topics are being most subscribed to across the event mesh?
A Sample Implementation
I’ve written a basic Node application that queries nodes of the event mesh and store it in a database using Prisma – a powerful JavaScript ORM library. I also wrote a GraphQL server that exposes the tables in Prisma via GraphQL. The utility currently stores and exposes client and topic subscriptions but can easily be extended to cover more use cases.
You can find the GitHub repo/setup instructions here.
Here are some sample queries and the results that you can get with this application stack:
Which node is my topic subscribed to from?
query{
findClientsForSubscription(topicString: "my/topic")
{
subscription
clients {
nodeName
}
}
}
Result:
{"data": {
"findClientsForSubscription": [
{
"subscription": "my/topic",
"clients": [
{
"nodeName": "Cloud Broker"
},
{
"nodeName": "Local Broker"
}
]
}
]
}
}
Which user and node is my topic subscribed to from?
Query{
findClientsForSubscription(topicString: "my/topic"){
subscription
clients {
nodeName
userName
}
}
}
Response:
{"data": {
"findClientsForSubscription": [
{
"subscription": "my/topic",
"clients": [
{
"nodeName": "Cloud Broker",
"userName": "local-user"
},
{
"nodeName": "Local Broker",
"userName": "default"
}
]
}
]
}
}
Conclusion
An event mesh is a powerful platform that dynamically routes events to their intended destination and nowhere else. GraphQL is a very powerful query language that is able to help you find answers to specific questions about your event mesh.
Explore other posts from category: For Developers

 Thomas Kunnumpurath
Thomas Kunnumpurath